
Locating the stockholders’ equity section on this statement is the primary step in calculating this crucial figure. When a company decides to distribute a portion of its profits to shareholders, it reduces retained earnings, thereby decreasing stockholders’ equity. The decision to pay dividends often reflects management’s confidence in the company’s future cash flows and its commitment to returning value to shareholders. However, excessive dividend payouts can strain a company’s financial resources, potentially limiting its ability to invest in growth opportunities. Stockholders’ equity is composed of several key elements that collectively provide a comprehensive picture of a company’s financial standing.
- In short, the asset value can be calculated by adding the firm’s equity and total debt or liabilities.
- The book value of an entire corporation is the total of the stockholders’ equity section as shown on the balance sheet.
- A higher ROE suggests stronger equity efficiency and shareholder value creation but must be assessed alongside leverage and industry context.
- Equity is important because it represents the value of an investor’s stake in a company, represented by the proportion of its shares.
- Retained earnings offer a glimpse into a company’s growth potential and financial discipline.
- This section of the balance sheet primarily consists of common stock and retained earnings.
Shareholders’ Equity vs Market Cap

The second is the retained how to determine stockholders equity earnings, which includes net earnings that have not been distributed to shareholders over the years. Determining stockholders’ equity practically involves examining a company’s financial statements, particularly its balance sheet. The balance sheet, often referred to as the statement of financial position, provides a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
Step 3: Subtract Total Liabilities from Total Assets
Investors seeking quality growth stocks use ROE analysis for investors to screen companies that demonstrate a history of efficient capital use and strong return generation. When combined with trend analysis, ROE becomes a predictor of future competitiveness. That part of the accounting system which contains the balance sheet and income statement accounts used for recording transactions. Some valuable items that cannot be measured and expressed in dollars include the company’s outstanding reputation, its customer base, the value of successful consumer brands, and its management team. As a result these items are not reported among the assets appearing on the balance sheet. For instance, if a corporation exchanges 1,000 of its publicly-traded shares of common stock for 40 acres of land, the https://flyfortune.in/2024/07/03/calculating-overtime-pay-a-guide-for-employers/ fair market value of the stock is likely to be more clear and objective.
- Another reason for setting a low par value is that when a company issues shares, it cannot sell them to investors at less than par value.
- At the end of 2021, the company reported the following carrying values on its balance sheet.
- Nowhere on the stock certificate is it indicated what the stock is worth (or what price was paid to acquire it).
- For instance, if a stock has a par value of $1 but sells for $10, the $1 is allocated to common stock, and the remaining $9 goes to additional paid-in capital.
- This prioritization provides preferred shareholders with an added layer of protection.
- Financial equity represents the ownership interest in a company’s assets after deducting liabilities.
How Do You Calculate Equity in a Private Company?
- It represents shares of a company’s own stock that it has repurchased from the open market.
- This preferred stock feature assures the owner that any omitted dividends on this stock will be made up before the common stockholders will receive a dividend.
- Treasury stock refers to shares that were once part of the outstanding shares of a company but were subsequently repurchased by the company itself.
- Persistent ROE significantly below industry averages, or negative ROE over multiple periods, often signals operational inefficiency or weak capital deployment.
- Think of retained earnings as savings because it represents a cumulative total of profits that have been saved and put aside or retained for future use.
The figures used to calculate the ratio are recorded on the company balance sheet. Treasury shares are shares repurchased from the open market and held in the company’s treasury. Share repurchases can increase the value of remaining shares by reducing supply or prevent hostile takeovers by decreasing available voting power.

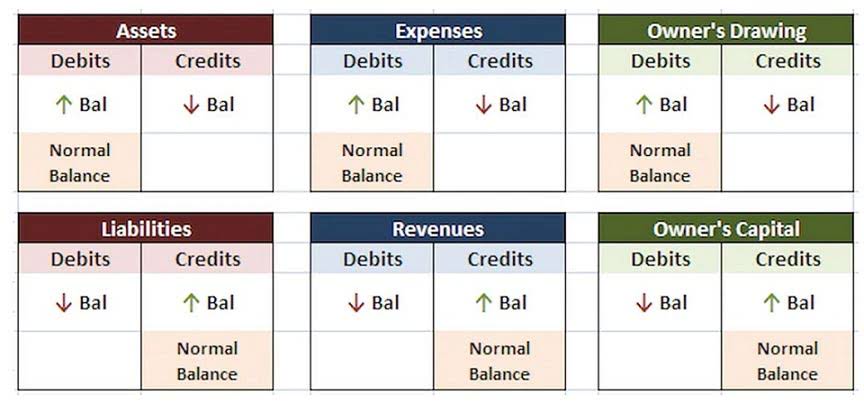
Amounts received for preferred stock above its par value are recorded as additional paid-in capital. The fundamental accounting equation states that the total assets belonging to a company must always be equal to the sum of its total liabilities and shareholders’ equity. When calculating the shareholders’ equity, all the information needed is available on the balance sheet – on the assets and liabilities side. The total assets value is calculated by finding the sum of the current and non-current assets.
Paid-in Capital or Contributed Capital

Each period, the net income or loss from the income statement is added to or subtracted from the beginning retained earnings balance. Shareholder equity (SE) is a company’s net worth, or its total assets minus its total liabilities. It is equal to the total dollar amount that would be returned to the shareholders if the company were liquidated and all its debts were paid off.
The above formula sums the retained earnings of the business and the share capital and subtracts the treasury shares. Retained earnings are the sum of the company’s cumulative earnings after paying dividends, and it appears in the shareholders’ equity section in the balance sheet. Stockholders’ equity refers to the What is bookkeeping residual interest in a company’s assets after deducting liabilities, representing the owners’ claim on the business. Net worth, often used interchangeably, typically applies to individuals, indicating the difference between personal assets and liabilities. In a corporate context, both terms reflect the company’s financial health, but “stockholders’ equity” is the precise term used in financial statements.
